Cryptocurrencies are digital money that operate without the involvement of centralized authorities. This means their exchange rate and supply are not controlled by any government institution, such as a central bank, or any individual.
The principles of fiat currency exchange rates are usually clear not only to experts but also to ordinary people, even those with a vague idea about economics or finance. However, the situation in the cryptocurrency market is quite different because crypto has nothing in common with fiat money. News headlines about sharp price jumps and drops in digital assets appear daily, making this market less predictable and much more volatile.
This is especially true for Bitcoin, the first and largest cryptocurrency, whose value can sometimes seesaw by 10% or more within a very short period.
So, what drives these dramatic fluctuations? To understand what affects cryptocurrency prices on exchanges, it is essential to grasp the key factors that directly or indirectly influence their value. Let's explore what determines the price of cryptocurrencies in this article.
What is cryptocurrency and where it came from

Cryptocurrencies are digital money that operate independently of centralized authorities. This means that neither their exchange rate nor their supply is controlled by any governmental institution, such as a central bank, or any individual.
At the heart of cryptocurrencies lies a technology similar to peer-to-peer networks, where files are stored and transferred between many users rather than being centralized on one server.
The lack of centralized control eliminates the need to entrust account management, balances, and transactions to a single governing body. This decentralization ensures greater transparency, reduces fraud risk, and prevents the double-spending of funds.
New cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, are created through a process known as "mining," in which computers solve complex mathematical problems. These problems are tied to encryption, ensuring transaction security and regulating the issuance of new cryptocurrency units.
Every network participant maintains a complete history of all transactions and account balances. This feature allows cryptocurrencies to track the entire path of any financial operation, making them transparent and more reliable.
Bitcoin is the first and most recognizable cryptocurrency, still holding the highest market value. It was created in 2009 by an individual or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto, whose true identity remains unknown.
Today, Bitcoin's popularity is so immense that all other digital currencies are commonly referred to as "altcoins," meaning alternatives to Bitcoin. Bitcoin's high price has driven investors to seek more affordable altcoins. These investors aim to find new alternative coins that could successfully compete with Bitcoin or, potentially, even replace it over time.
Many of these alternative cryptocurrencies are designed to address issues inherent to Bitcoin, such as its limited supply. To date, Bitcoin significantly outpaces even the most successful altcoins in terms of market capitalization.
In 2009, however, the now-leading cryptocurrency was virtually unknown to the general public. At that time, cryptocurrency was just beginning its journey and held little value for users. A few dollars could buy thousands of bitcoins.
Like any currency, cryptocurrencies gain value as interest and community participation grow. However, since most digital currencies are issued by private companies working with blockchain technology, the value of these assets also depends on the reputation and success of these corporations, including the viability of their projects and perceived utility.
Key factors: supply and demand
The primary factor determining cryptocurrency prices is the balance between supply and demand. This is a basic economic principle. If there is an abundance of a particular cryptocurrency's tokens in the market but low demand for them, their price will fall. Conversely, if supply is limited and interest is high, the coin's value will rise.
Key factors influencing cryptocurrency prices
As of July 2024, there are approximately 15,000 coins and tokens globally, including 53 stablecoins. These crypto assets are pegged to the value of other financial instruments. For example, the price of Tether (USDT), launched in 2013, consistently remains at $1, while other cryptocurrencies can experience significant price fluctuations.
The price of cryptocurrencies is influenced by several factors:
- Supply and demand
- News coverage
- Regulatory policies
- Competition among cryptocurrencies
- Production costs (for Proof-of-Work-based crypto assets)
Let’s explore each factor in more detail.
Supply and demand
The price of any asset is influenced by a few key factors. When demand for a cryptocurrency increases while the supply is limited, its price rises. Conversely, if supply grows suddenly while demand remains the same, the asset's price decreases.
Many digital assets are issued in unlimited quantities. However, there are cryptocurrencies with highly restricted supplies, such as Bitcoin, Litecoin, and Dogecoin.
News
News is a primary driver of demand for cryptocurrencies. Information about significant updates, new partnerships, the implementation of cutting-edge technologies, and other crucial events can greatly increase investor interest in a particular cryptocurrency.
Media coverage of blockchain industry events has a direct impact on cryptocurrency market quotes. For instance, if large companies start using Bitcoin in their operations or if government agencies unexpectedly recognize digital currencies, their value is bound to rise.
Negative news, however, can have the opposite effect, leading to the sell-off of cryptocurrencies. For example, sudden regulatory tightening, cyberattacks on platforms, or sharp statements from influencers (such as Elon Musk) can trigger a rapid decline in the price of specific cryptocurrencies.
Example: The price of the BAT token, part of the Brave browser ecosystem, fell sharply from $0.25 to $0.23 on June 6 after a user discovered that the browser's search bar was automatically inserting referral links to popular crypto exchanges. However, the price soon recovered to its original level.
Another example is the Theta Fuel token, which gained over 700% in late May 2021. This surge likely resulted from the launch of the Theta mainnet and the integration of the Theta app into Samsung Daily on Galaxy devices.
Production costs
Some cryptocurrencies, such as BTC, BCH, KAS, LTC, and DASH, are mined through a process that involves solving unique identifiers for new blocks in decentralized networks, requiring substantial computational resources.
Miners invest heavily in specialized equipment and bear ongoing costs for its maintenance and electricity. Given the high expenses, miners rarely sell their coins below a certain price, which can result in an accumulation of coins in wallets, creating market shortages and driving up prices.
Competing coins
The crypto market features numerous assets competing for investor interest. As of July 24, 2024, Bitcoin (BTC) accounted for 54.9% of the total cryptocurrency market capitalization, with this percentage fluctuating constantly.
When Bitcoin’s dominance weakens, its price relative to other cryptocurrencies tends to decline. Conversely, when its market share increases, Bitcoin prices commonly rise.
Regulatory policies
The introduction of favorable new laws can boost asset values, while restrictions and bans often lead to price drops for coins and tokens. Thus, news and information about cryptocurrency regulation can have a significant impact on their prices.
Example: In 2017, Japan recognized Bitcoin as a legal means of payment, triggering a rapid rally. Conversely, China's decision to ban cryptocurrency transactions caused a drop in BTC prices.
In 2024, the regulation of the cryptocurrency market remains an open question. The industry continues to evolve rapidly, with new products and technologies emerging, keeping investors closely monitoring regulatory statements and decisions worldwide.
Other meaningful factors
Due to the sensitivity of financial markets, cryptocurrency prices can be affected by a wide range of events, from minor incidents to major developments. Below are additional factors:
| Factors | Explanations |
| Innovations | New technologies and upgrades to existing systems can increase crypto value |
| Global economy | Economic conditions, crises, and living standards impact crypto prices |
| Manipulation | Large investors (“whales”) can cause price swings through strategic buying/selling |
| Crypto community | The level of activity within blockchain projects can affect asset values |
Bitcoin and fiat currency exchange rates

Fiat money and cryptocurrencies operate on different principles. National currencies are managed centrally, such as the US dollar, controlled by the Federal Reserve. The Fed can weaken the dollar using tools like interest rate cuts, quantitative easing, or currency interventions.
Fiat currency prices are closely tied to economic conditions. During economic downturns, fiat values often decrease, while stable economies strengthen them.
Cryptocurrencies, however, are decentralized, and their value does not depend on the economic conditions of individual countries or the policies of central banks.
Initially, Bitcoin's price was determined by mining costs, including electricity and equipment expenses. However, as Bitcoin began trading on crypto exchanges and attracting significant investor attention, its price became increasingly influenced by supply and demand dynamics.
In 2017, Bitcoin's price skyrocketed from less than $1,000 at the beginning of the year to nearly $20,000 by December, driven by buoyant interest and demand. Conversely, in 2018, regulatory restrictions in Asia led to decreased demand, causing prices to drop.
In conclusion, while it's impossible to list all factors influencing cryptocurrency prices, the key drivers include demand, supply, regulatory changes, production costs, competition, and innovation. The cryptocurrency market remains dynamic, making it essential for investors to stay informed and vigilant.
Market capitalization and circulating supply

The price of a cryptocurrency is influenced not only by its total supply but also by the number of coins currently in circulation. The more coins available on the market, the higher the likelihood of downward pressure on their price.
Take Bitcoin as an example. Its total supply is capped at 21 million coins, a limit set by its creator. Currently, about 18.4 million Bitcoins are in circulation, with miners adding approximately 900 BTC daily. When miners sell their newly mined coins, they increase the market supply, which can contribute to a decline in price.
Many economists argue that the fixed supply of 21 million coins is insufficient for the full functioning of an economy. Unlike the current monetary system, where banks can create an unlimited amount of money (e.g., through credit issuance), Bitcoin's supply is strictly limited. Over time, the value of traditional fiat currencies, such as the US dollar, erodes due to inflation.
Bitcoin's principles of operation were inspired by precious metals, particularly gold. Like gold, Bitcoin relies on the principle of resource scarcity to maintain its value. Just as Earth's gold reserves are finite and may eventually be exhausted, Bitcoin also has a supply cap.
When all Bitcoins are mined, or when the cost of mining becomes prohibitively high, the issuance of new Bitcoins will cease. Bitcoin advocates argue that the cryptocurrency can be divided into smaller units, and its value will likely increase as the supply cap is reached.
Reducing circulating supply

Various mechanisms have been developed to reduce the number of coins in circulation. For instance, after the Ethereum network update, staking came into being. This feature allows users to earn passive income by holding ETH, reducing their inclination to sell and thereby decreasing the circulating supply.
Market capitalization
Market capitalization is another crucial factor directly influencing cryptocurrency prices. It is calculated by multiplying the coin's price by the total number of tokens issued. The higher the market capitalization, the more effort is required to influence the price.
Cryptocurrencies with low market capitalization can experience sharp increases of hundreds or even thousands of percent over a short period, but they are also more vulnerable to manipulation. For example, in November, the token ParallelCoin, with a market cap of just $53,000, surged by 400,000% in a single day.
Trading volume
Trading volume also significantly affects the value of crypto assets. Low trading volume may indicate low demand for a cryptocurrency and make its price easier to manipulate.
Usage and features
Another factor driving demand and increasing cryptocurrency value is its use case. Let’s consider Binance’s BNB token as an example. In December 2018, its price hit a low of $4.20. However, in early 2019, Binance announced the launch of a platform for initial exchange offerings (IEOs), requiring BNB tokens for participation. This announcement led to a rapid price increase, reaching a high of $39.60 by July.
Other exchange cryptocurrencies, such as those from KuCoin, OKEx, and Huobi, demonstrated similar dynamics after launching their IEO platforms.
Token burning
Another notable feature of the BNB token is Binance’s quarterly token burns. In April, the company burned tokens worth $52.5 million, reducing the total circulating supply, which in turn increased demand for the token.
Product and users

The existence of a functioning product also significantly impacts cryptocurrency prices. Cryptocurrencies vary in purpose. For instance, Bitcoin serves as a payment system and an investment asset but is not directly tied to any specific product.
In contrast, consider the Enjin token. Its underlying project offers various solutions, including a blockchain explorer, a wallet, and a platform for trading gaming items with over 20 million users.
This practical application likely contributed to Enjin’s stronger recovery compared to Bitcoin during the market downturn. In March, Enjin’s price dropped from $0.91 to $0.032 but later surged by nearly 500%, reaching $0.19 and briefly exceeding $0.23. In comparison, Bitcoin’s price increased by only 150% during the same period.
Correlation with Bitcoin
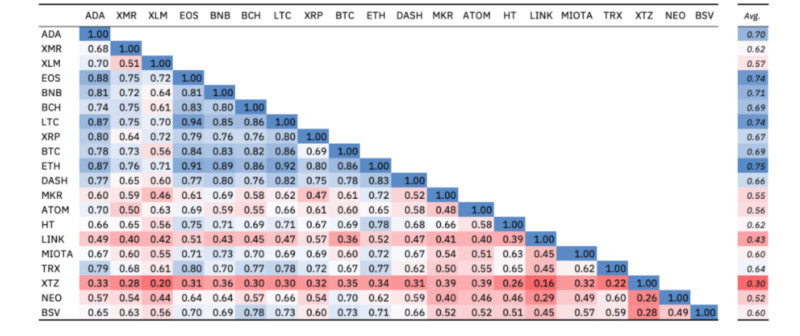
For most cryptocurrencies, price correlation with Bitcoin is a significant factor. Historical trends show that when Bitcoin rises or falls, altcoin prices often follow suit.
For example, a Binance study found that Ethereum, Litecoin, EOS, XRP, Bitcoin Cash, and BNB prices followed Bitcoin’s movement 70% of the time. However, tokens like Atom, Link, and Tezos showed a lower correlation, with their prices ranging from 24% to 28%.
Key considerations
Numerous factors influence cryptocurrency prices, and some—like token supply and practical applications—require constant monitoring. Understanding these critical aspects can help investors select coins with lower risks and higher growth potential.
However, unpredictable factors, such as news (both positive and negative), also play a significant role. High-impact events can impact the entire crypto market, so staying informed about current developments is crucial for anyone investing in digital assets.
Tracking news can be challenging, but it can lead to substantial profits under favorable conditions. To stay updated on critical events in the crypto industry, investors can use specialized tools and applications.
When planning and making decisions about cryptocurrency investments, always consider all factors simultaneously. Besides, remember Warren Buffett’s advice: "Be fearful when others are greedy and greedy when others are fearful." This unconventional approach can often lead to successful cryptocurrency investments.







 Back to articles
Back to articles



